






SoundPNEI® APPLICATIONS Private Users Physicians Not Medical Practitioners Psychologists |
LA RICERCA - RESEARCHES:
Pubblicazioni PubMED a riguardo PubMED Publications La maggiore fonte di verifica degli effetti delle vibrazioni sonore sul corpo umano sono le centinaia di casi trattati con risultati tangibili e misurabili dagli stessi utenti in molteplici tipologie di disturbi, anche gravi. La ricerca scientifica, allo stato attuale, ci mette a disposizione studi che validano il nostro approccio, dimostrando la relazione diretta tra le proprietà biofisiche del suono e le funzioni cellulari dell'uomo e degli organismi viventi. La biofisica, e la bioacustica in particolare, sono materie con ampi margini di indagine e di approfondimento e che destano l'interesse dell'intera comunità scientifica internazionale, impegnata in vari fronti di ricerca in questo settore. Ma quello che già conosciamo è sufficente ad ottenere risultati sorprendenti, nel campo del benessere e della salute, attraverso l'utilizzo della tecnica bioacustica SoundPNEI®. Qui sulla destra, un estratto di alcune delle più recenti ricerche scientifiche sugli effetti biologici delle vibrazioni acustiche.
The most important way to monitor the effects of sound vibrations on the human body are the results of hundreds of cases treated. SoundPNEI® users have been able to measure clearly the improvements made in different types of disorders, even severe.
Scientific research, at the current state, has made available the results of studies that validate our approach, demonstrating the direct relationship between the biophysical properties of the sound vibrations and the cellular functions of humans and living organisms. Biophysics, and in particular bioacoustics, are a matter yet to be deeply investigated that arouses the interest of the entire international scientific community, working, all over the world, on various fronts of research in this area. But what we already know about, it's enough to obtain surprising results for health and wellness, applying the SoundPNEI® bioacoustic technique . On the right, an excerpt of some of the latest research on the biological effects of acoustic vibrations. |
Direct effects of music in non-auditory cells in culture.
Lestard Ndos R, Valente RC, Lopes AG, Capella MA. Source Institute of Biophysics Carlos Chagas Filho; Institute of Medical Biochemistry, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. 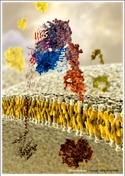 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23955127 Optical measurements of long-range protein vibrations
Gheorghe Acbas, Katherine A. Niessen, Edward H. Snell & A.G. Markelz 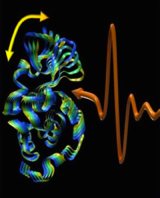 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24430203 Growth and physiological characteristics of E. coli in response to the exposure of sound field. Gu SB, Yang B, Wu Y, Li SC, Liu W, Duan XF, Li MW. Author information: College of Food and Bioengineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, People's Republic of China. 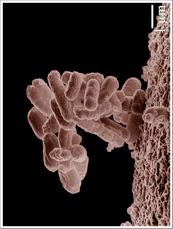 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24502157 Life Rhythm as a Symphony of Oscillatory Patterns: Electromagnetic Energy and Sound Vibration Modulates Gene Expression for Biological Signaling and Healing
Affiliations: Visual Institute of Developmental Sciences, Bologna, Italy (Dr Muehsam). National Institute of Biostructures and Biosystems, Visual Institute of Developmental Sciences, Bologna; Department of Experimental, Diagnostic and Specialty Medicine, University of Bologna (Dr Ventura), Italy.  http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24808981
Biological Effect of Audible Sound Control on Mung Bean (Vigna radiate) Sprout W. Cai, 1 H. He, 2 S. Zhu, 2 ,* and N. Wang 3 ,* Ningbo Institute of Technology, Zhejiang University, 1 Qianhu South Road, Ningbo, Zhejiang 315100, China Key Laboratory of Equipment and Informatization in Environment Controlled Agriculture, Zhejiang University, 866 Yuhangtang Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310058, China Department of Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering, Oklahoma State University, 111 Ag Hall, Stillwater, OK 74078, USA 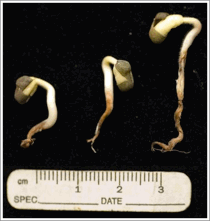 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25170517 PUBMED
US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health PubMed comprises more than 24 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. |